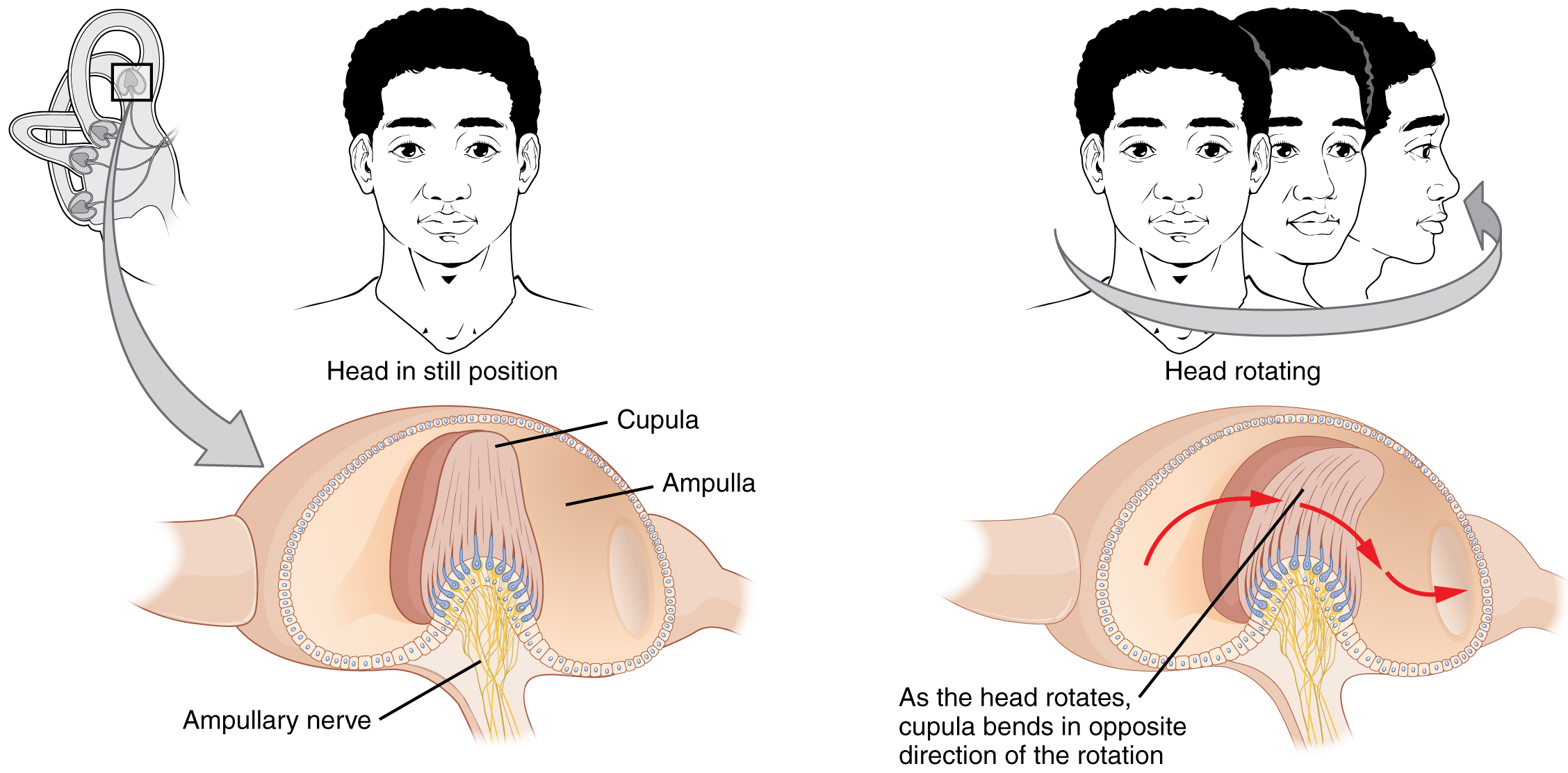
The vestibular part or non-auditory part of the internal ear is concerned with the Physiology of Balance and Equilibrium. The receptor apparatus in the ampulla is crista-ampullaris. It consists of the cupola which is a gelatinous wedge shaped structure running fully across the cross-section of the ampula. Into the thick end of this wedge projects a ridge carrying many hair cells whose processes are embedded in cupola. The utricle and saccule have a patch or macula of hair cells that are also projecting into and embedded in gelatinous mass. This also contains above the hairs an otolith composed of a mass of calcium carbonate crystals called otoconia.
The vestibular system is affected by linear and rotational movements of the head. Classically, semicircular canals respond to angular accelerations and the otolinth organs of the utricle and saccule respond to the direction of gravity force and to linear acceleration.
Functions of Vesticular System :
- It contributes to the sensation of motion and of spatial orientation of the head.
- During head movement, it helps to maintain a stable image on the retina by causing compensatory eye movements.
- It contributes to the maintenance of balance and various postures.
Movement of the head cause flow of endolymph and deflection of cupola of crista-ampularis.As a result of these hairs get bend. As a result impulses are generated in hair cells and are passed on through vestibular branch of VIII cranial nerve to the brain. Similarly flow of endolymph in otolith organ of utricle and saccule causes the movement of hairs of the hair cells. This causes generation of action potential discharge which is passed on to the brain through vestibular branch of VIII cranial nerve. In brief static equilibrium is the orientation of the body relative to the pull of gravity. The macule of utricle and saccule are the sense organs of static equilibrium. Dynamic equilibrium is the maintenance of body position in response to movement. Crista ampullaris is the sense organ for the dynamic equilibrium.
Vestibular Disease:
There are a variety of diseases of the inner ear which are characterized by vertigo, severe dizziness, and tinnitus or ringing in the ears and deafness. The vertigo is often so severe that there is nausea and vomiting, blurred vision, a tendency to fall in a certain direction and nystagmus. Nystagmus is characterized by rapid, involuntary movement of the eyeballs. Electronystagmography is a diagnostic test that is useful in identifying vestibular diseases. Electrodes are placed on each side of the face to measure movement of the eye while they are closed.
Otitis media:
It is discharge of pus from middle ear with rupture of the drum. Also view more useful articles by PCD Pharma Company.
 Enquiry
Enquiry