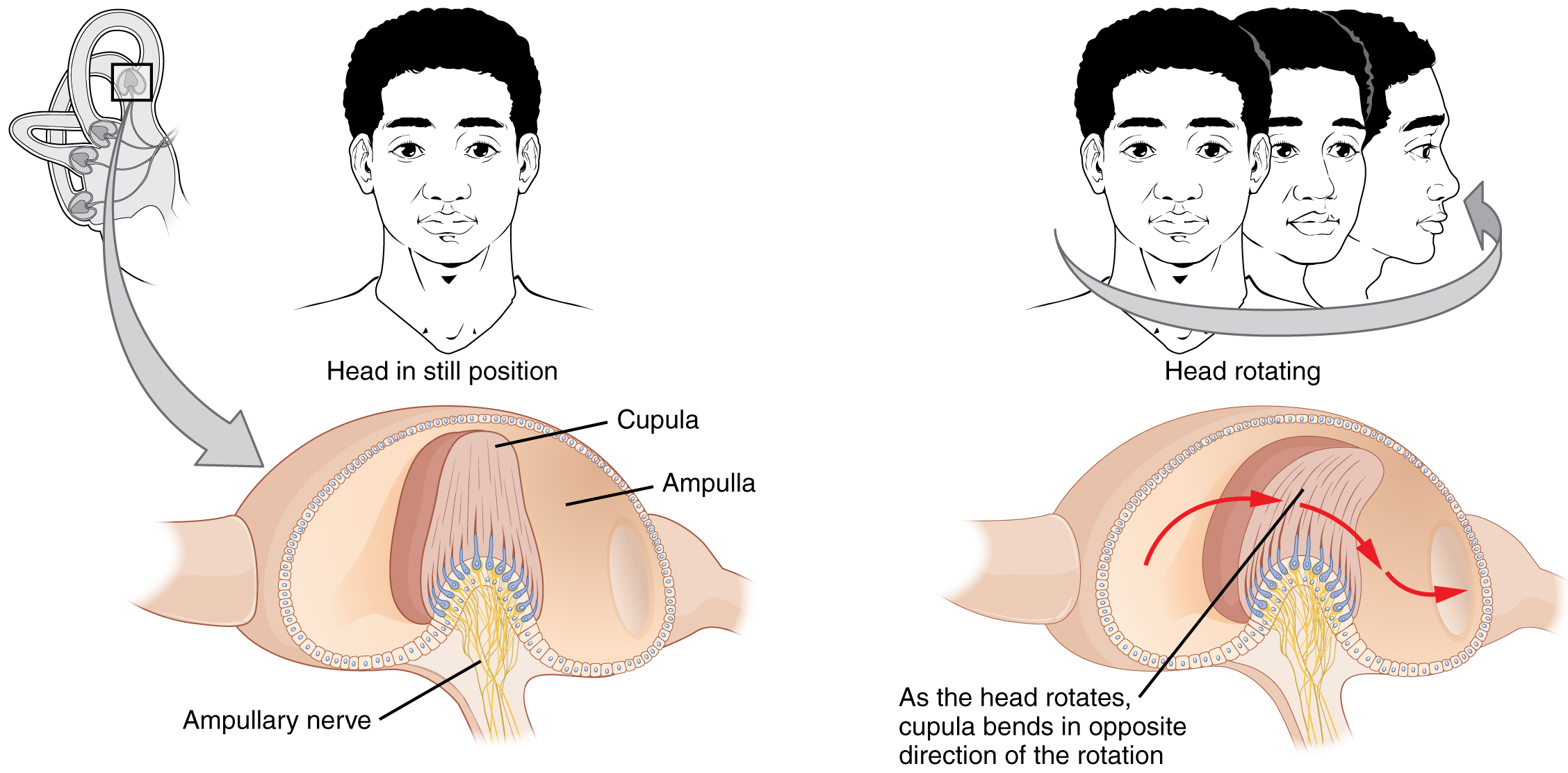
The vestibular part or non-auditory part of the internal ear is concerned with the Physiology of Balance and Equilibrium. The receptor apparatus in the ampulla is crista-ampullaris. It consists of the cupola which is a gelatinous wedge shaped structure running fully across the cross-section of the ampula. Into the thick end of this wedge projects … Continue reading Physiology of balance and equilibrium
Month: November 2013
Structure of Pancreas
Pancreas is a mixed type of gland consisting of two parts: Exocrine part and Endocrine part. The bulk of the Pancreas consists of glandular acini which secrete a powerful digestive juice into the gut. This is the exocrine part of the pancreas. Scattered amongst the acini are tiny clumps of cells known as the islets of Langerhans. This is the endocrine … Continue reading Structure of Pancreas
What is the Physiology of Vision?
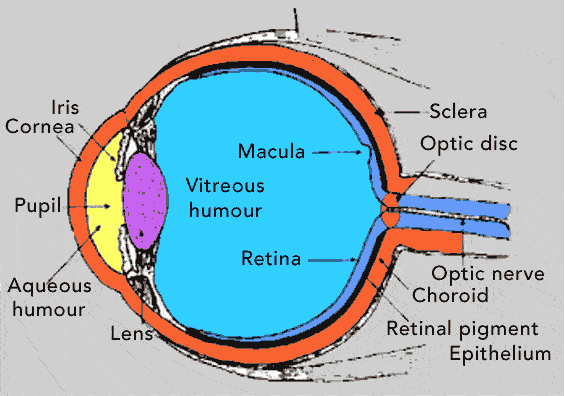
Before light can reach the rods and cones of the retina, it must pass through the cornea, aqueous humor, pupil, lens and vitreous humor. The first step in Physiology of Vision is retinal image formation and activation of Photoreceptors. The resulting nerve impulses are then passed to the visual areas of the cerebral cortex. Retinal … Continue reading What is the Physiology of Vision?
 Enquiry
Enquiry